Most cyberattacks don’t start with alarms. These begin quietly and go through networks unnoticed until data is stolen, systems fail, or operations come to a standstill. It is usually too late by the time the damage is evident.
Network intrusion detection provides organizations with the possibility of identifying suspicious activity and malicious behavior in real-time. Intrusion detection systems do not respond to a breach, but instead they scan network traffic in real time to reveal threats that are missed by conventional defenses.
A network intrusion detection system (NIDS) offers the visibility required to identify known attacks, abnormal behavior and unauthorized access early. This guide will teach you the operation of network intrusion detection, the key types of IDS, and the tools and best practices that can be used to protect current networks.
What is Network Intrusion Detection?
Network intrusion detection is the work of checking a network on suspicious activity or unauthorized access. Its main aim is to recognize possible threats, malware or attacks on the fly, in order to enable organizations to react before massive damage is done.
In contrast to firewalls, which prevent some traffic, intrusion detection systems center on identifying anomalies and malicious action in network traffic.
Intrusion detection has two primary types of systems, which are IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention System). An IDS notifies the administrators of suspicious activity, whereas an IPS proactively blocks or reduces the threat. The distinction between IDS and IPS is important to consider when designing a network intrusion detection policy.
Network intrusion detection systems have more advantages than threat alerts. They enhance visibility of the entire network, assist organizations in meeting regulatory mandates, and offer important data to analyze incidents. With the help of the IDS in your cybersecurity plan, companies will be able to secure sensitive data, minimize downtime, and improve their protection against internal and external attacks.
How Network Intrusion Detection Works
Network intrusion detection is based on observing and examining network traffic in order to identify suspicious or malicious activity. Three major detection methods are in use:
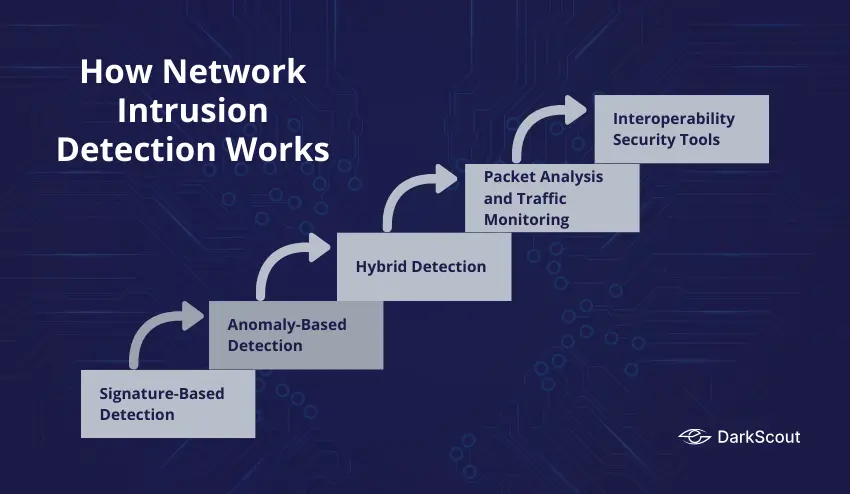
1. Signature-Based Detection
This technique matches network traffic to a list of known threat signatures. In case of a match, the system sends an alert. The signature-based detection works well in detecting a known attack but fails to detect a new or unknown threat.
2. Anomaly-Based Detection
Anomaly-based detection compares normal network behavior and indicates an anomaly with the baseline. This technique is an effective proactive network intrusion detection tool because it is able to detect zero-day attacks and abnormal patterns.
3. Hybrid Detection
Other systems integrate signature and anomaly methods, providing a middle ground solution that will be able to identify both known and new threats. Hybrid systems are more covered and less false positives.
4. Packet Analysis and Traffic Monitoring.
The intrusion detection systems scan packets that traverse the network, and compare patterns in real time. IDS can identify malicious traffic by looking at packet header, payloads, and traffic pattern, including port scanning, suspicious logins, or malware traffic.
5. Interoperability with Other Security Tools.
In today’s IDS, they are often included as part of firewalls, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, and endpoint protection platforms that allow for faster response time and greater visibility across the network creating a better security posture.
Understanding how a network intrusion detection system operates will give organizations the ability to choose the proper approach, tool, and configuration to protect their networks.
Types of Network Intrusion Detection Systems
Organizations need network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) in three primary forms, which are typically used depending on organizational requirements:
1. Network-Based IDS (NIDS)
NIDS is a network traffic monitoring tool that operates at strategic locations like routers and switches to identify suspicious network traffic. It scans the packets entering and leaving the system and notifies the administrators of possible risks.
- Advantages: Gives a general perspective of the traffic on the network; may identify attacks on more than one device.
- Disadvantages: Low visibility of encrypted traffic; sensor positioning is paramount to success.
2. Host-Based IDS (HIDS)
HIDS is deployed on individual devices or servers and scans system logs, file integrity, and local activity to identify intrusion. It is good to identify attacks not captured by network monitoring.
- Advantages: In-depth understanding of single host activity; capable of identifying insider threats.
- Disadvantages: Intensive in resources; must be installed and maintained on every host.

